Medical Insights: Comprehensive Collection of Medical Algorithms
Medical algorithms are mathematical models used to make decisions in the field of medicine. These algorithms take into account a variety of factors, including patient symptoms, medical history, and test results. They are used to support decision-making in a wide range of areas, including diagnosis, treatment planning, and clinical research.
Medical algorithms can be based on statistical methods, machine learning, or other artificial intelligence techniques. Most practitioners use only a small segment of algorithm medicine routinely. However, there is a growing need for algorithms in healthcare as the volume of medical data increases.
What is a Clinical Practice Algorithm?
A clinical practice algorithm is a systematic, graphical representation designed to assist healthcare professionals in making decisions about the appropriate healthcare for specific clinical circumstances. It integrates a clinical algorithm, which is essentially a step-by-step protocol, aimed at standardizing the approach towards diagnosis, treatment, or management of a particular condition. The concept of an algorithm in medicine transcends simple decision trees; it encompasses comprehensive guidelines that incorporate evidence-based practices and clinical expertise to ensure patient care is both efficient and effective.
The algorithm medical definition extends to a wide range of applications, from diagnostic processes to therapeutic management and patient monitoring. For instance, a medical diagnosis algorithm simplifies complex decision-making by providing a structured pathway for evaluating symptoms, signs, and test results, leading to a differential diagnosis or a definitive diagnosis. This not only enhances the accuracy of diagnoses but also improves patient outcomes by facilitating timely and appropriate interventions.
Examples of medical algorithms include protocols for the management of chronic diseases like diabetes and hypertension, where specific steps guide the adjustment of medications based on patient response. Similarly, algorithms are used in emergency medicine for conditions such as acute myocardial infarction or stroke, where rapid decision-making is critical to achieving the best possible outcomes. These examples highlight how clinical algorithms are indispensable tools in modern healthcare, optimizing patient management through standardized, evidence-based approaches.
The development and implementation of an algorithm in medicine are grounded in clinical research and consensus among healthcare professionals. By following a medical diagnosis algorithm, clinicians can navigate the complexities of patient care with greater confidence and precision. Moreover, these healthcare algorithms are regularly updated to reflect the latest advancements in medical science and technology, ensuring that the care provided is aligned with the current best practices. In summary, the application of clinical algorithms in healthcare represents a cornerstone of quality patient care, epitomizing a methodical and evidence-based approach to medical decision-making.
Types of Medical Algorithms
Diagnostic Algorithms
An algorithm for medical diagnosis can be used for healthcare in a number of ways. It can be used to determine which tests should be performed, how to interpret test results, and what the best course of treatment is. In some cases, medical algorithms for diagnosis are also used to predict how likely a person is to develop a certain condition or respond to a particular treatment. A diagnosis algorithm has the potential to improve the accuracy and efficiency of healthcare diagnosis and treatment.
There are a number of benefits to using a diagnosis algorithm in healthcare. An algorithm for medical diagnosis can help to improve the accuracy of diagnoses, as well as the efficiency with which they are made. In some cases, they may also be able to reduce the cost of healthcare by avoiding unnecessary tests or treatments.
Treatment Algorithms
Before the immediate access to medical data we have today, healthcare providers relied on their own knowledge and the advice of their colleagues with whom they would deliberate on difficult to determine diagnosis. But now, we have the capability to incorporate a medical treatment algorithm into everyday clinical practice.
A medical treatment algorithm can be used for treatment planning in a variety of ways. It can be used to generate a list of potential treatments, to prioritize treatments, or to select the most effective treatment based on the individual patient's needs. A treatment algorithm can also be used to monitor patients for early signs of disease progression or to identify which patients are at risk for complications. In addition, treatment algorithms in healthcare can be used to develop new treatments or to improve existing ones.
Clinical Research
Algorithms in healthcare are increasingly being used in clinical research to help identify potential treatments and improve patient outcomes.
One way is to use healthcare algorithms to identify potential treatments for a particular condition. By inputting data about a patient's symptoms, medical history, and other factors, algorithms in healthcare can generate a list of possible treatments that might be effective. This can save a lot of time and effort for researchers who would otherwise have to manually search through medical literature to find potential treatments.
Another way that medical algorithms can be used in clinical research is to predict patient outcomes. By inputting data about a patient's condition, medical history, and other factors, medical algorithms can generate predictions about how that patient is likely to respond to different treatments. This can help researchers choose the most effective treatment for each individual patient.
Medical algorithms are still in the early stages of development. However, there is no doubt that the importance of medical algorithms to revolutionize clinical research has enormous potential.
Predictive Algorithms
Leveraging vast amounts of medical data, predictive algorithms use statistical techniques and machine learning to forecast future health events or outcomes in patients. These can range from predicting the risk of developing certain conditions, like diabetes or cardiovascular diseases, to forecasting patient outcomes after specific treatments. Predictive algorithms in medicine are instrumental in preventive medicine and personalized care, allowing for interventions before conditions become more severe.
Prescriptive Algorithms
Going a step beyond predictive algorithms, prescriptive algorithms analyze data to recommend specific actions that can improve patient outcomes. These might suggest lifestyle modifications, preventive measures, or therapeutic interventions tailored to the individual's risk factors and current health status. Prescriptive algorithms are a key component of personalized medicine, optimizing healthcare interventions for individual patients.
The utilization of algorithms in medicine, through the development and application of clinical algorithms, diagnostic algorithms, treatment algorithms, predictive algorithms, and prescriptive algorithms, represents a significant advancement in medical science. These tools not only streamline the diagnostic and treatment process but also enhance the quality of care, making healthcare more precise, personalized, and effective. Examples of medical algorithms are increasingly found in various medical software, electronic health records, and clinical decision support systems, illustrating their integral role in modern healthcare.
Why Healthcare Needs Medical Algorithms
Algorithms in healthcare are increasingly being used as the volume of healthcare data that needs to be processed grows larger. Medical algorithm effectiveness can help doctors sift through this data and find patterns that may otherwise be missed.
It’s no secret, the human body is complex and trying to diagnose our illnesses can be quite a task, even for the most seasoned doctors. To better their diagnoses, doctors collect as much information as possible from their patients. This information comes in an array of sources, including doctor’s notes, clinical images, genetic tests, demographics, and laboratory results. Today, databases of electronic health record systems contain data for billions of patients. But, despite all that data available and the best practices of physicians, misdiagnoses still happen on a daily basis.
The clinical environments physicians are required to think and act during the diagnostic process can be high-pressured, and in some cases, extremely time sensitive. Dealing with uncertainty is difficult. All this pressure in the accelerated healthcare environment can result in diagnostic errors, especially when a doctor runs into problems collecting or understanding information pertaining to physical examinations, patient history, or tests. Things are typically not straightforward when a patients’ condition counts are constantly progressing and evolving over time.
One way to help physicians improve their diagnostic accuracy is by helping them interpret data more efficiently. With this goal in mind, and as computers become more powerful, physicians are looking to software systems with medical treatment algorithms that can think like doctors, only faster and more efficiently. Workflows that integrate artificial intelligence in healthcare such as medical machine learning and NLP technology often aim to identify unstructured data in text notes, voice recordings and PDF documents in record time.
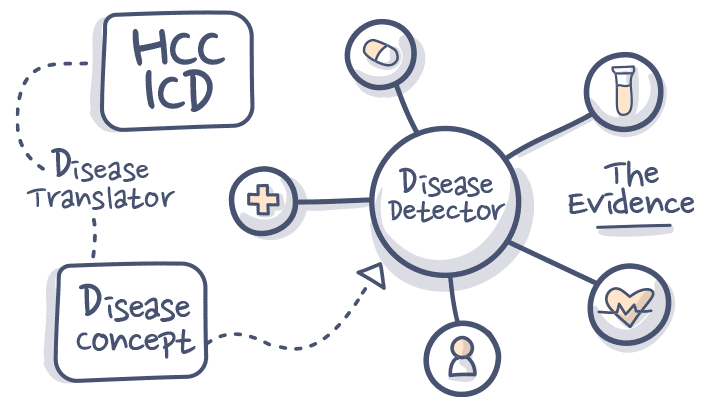
Some proprietary healthcare algorithms can detect specific diseases based on evidence in the patient record and predict a RAF score. The resulting information can help make a clinical diagnosis more complete and help to narrow down difficult to determine diagnosis. This can generate information crucial to the clinical process like determining a patient’s disease burden for risk adjustment coding.
Barriers to Usage
Medical algorithms for diagnosis would be more broadly used if they were easily accessible in a usable medical algorithms app format to clinicians, educators and researchers.
Some of the barriers to the usage of medical algorithms include the scarcity of knowledge that they even exist, uncertainty about their capabilities, difficulty in understanding the results expressed in the algorithm, and lack of access at the point of care. Automation of a treatment algorithm can serve to both share the medical information, as well as help in the correct application of that information with less errors, saving staff countless hours of dealing with denials and clerical bottlenecks.
Looking Forward
It’s understandable that medical algorithms are one essential format for sharing medically pertinent information, and that the sharing of that information is needed for safe patient care. Since the final responsibility for proper use remains with the clinician, there is a great need for medical algorithms to enable the easy capture of relevant information. Medical algorithms should be used primarily as a tool to reduce overall burdens of physicians and not to replace them. The development of algorithm medicine in healthcare presents an exciting and promising era in diagnosis. An era in which important medical advice can be made accessible, and more physicians and patients can benefit from it.
Want to Use Medical Algorithms to Better Diagnose Your Patients?
ForeSee Medical’s risk adjustment software works where you need it, at the point of care. Our proprietary healthcare algorithms and machine learned natural language processing rationalizes your patient data across the healthcare system. Then, we empower you with insightful HCC risk adjustment coding support and integrate it seamlessly with your EHR.